Release 8.1.5
A67439-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Parallel Server Setup and Configuration Guide Release 8.1.5 A67439-01 |
|
This chapter describes how instances are managed through initialization files and Oracle Parallel Server Management.
Specific topics covered in this chapter are:
An initialization parameter file is an ASCII text file containing a list of parameters.
Each node consists of an initialization parameter file named INITSID.ORA with parameters unique for an instance and an initialization parameter file named INITDB_NAME.ORA with common parameters shared from node-to-node.
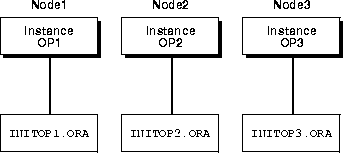
The INITSID.ORA instance initialization parameter files point to the INITDB_NAME.ORA file for common parameters and define the following for each instance:
The SID is the value of the DB_NAME parameter in the INITDB_NAME.ORA file and the thread ID. For instance, if the DB_NAME is OP, and the first node has a thread ID of 1, its SID is OP1; the second node uses the SID OP2 to identify its instance; and so on.
Figure 6-2 and Figure 6-3 show the contents of an initialization files for two nodes with node numbers of 1 and 2 were created by the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant:
ifile=C:\Orant3\admin\op\pfile\initop.ora rollback_segments = (rbs1_1,rbs1_2) thread=1 parallel_server=true instance_name=op1 remote_login_passwordfile=exclusive
ifile=C:\Orant3\admin\op\pfile\initop.ora rollback_segments = (rbs2_1,rbs2_2) thread=2 parallel_server=true instance_name=op2 remote_login_passwordfile=exclusive
The parameters are described below
INITDB_NAME.ORA database initialization file is called by the individual parameter files through the IFILE parameter.
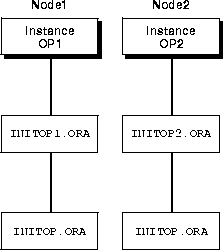
For Oracle Parallel Server, some initialization parameters must have the same values for every instance, whether individual or common parameter files are used. By referencing the common parameter file using the IFILE parameter within the individual parameter files, instances that have individual parameter files can use the correct parameter values for those that must be identical. This also allows individual parameter files with different values.
Figure 6-5 shows a INITDB_NAME.ORA file (INITOP.ORA) created for a Hybrid database through the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant:
db_name = op db_domain = us.oracle.com service_names = op.us.oracle.com db_files = 1024 control_files = ("\\.\op_ctl1", "\\.\op_ctl2") db_file_multiblock_read_count = 8 db_block_buffers = 2843 shared_pool_size = 15728640 log_checkpoint_interval = 10000 log_checkpoint_timeout = 0 processes = 50 parallel_max_servers = 5 log_buffer = 32768 max_dump_file_size = 10240 # limit trace file size to 5M each global_names = true oracle_trace_collection_name = "" background_dump_dest = C:\Orant3\admin\op\bdump user_dump_dest = C:\Orant3\admin\op\udump db_block_size = 8192 distributed_transactions = 10 compatible = 8.1.3.0.0 sort_area_size = 66560
Parameters to take note of:
See Oracle8i Reference for a description of the other parameters.
This section describes the following:
Initialization parameters with the prefix GC (Global Constant) are relevant only for an Oracle Parallel Server. These parameters are specified in the INITDB_NAME.ORA file.
Global constant parameter settings determine the size of the collection of global locks that protect the database buffers on all instances. The settings you choose affect the use of certain operating system resources.
Of the instances (OP1, OP2, and so on), the first instance to start up in shared mode determines the values of the global constant parameters for the other instances. The control file records the values of the GC_* parameters when the first instance starts up.
When another instance attempts to start up in shared mode, the Oracle Server compares the values of the global constant parameters in its parameter file with those already in use and issues a message if any values are incompatible. The instance cannot mount the database unless it has the correct values for its global constant parameters.
The global constant parameters for an Oracle Parallel Server are:
Multiple instance issues concerning initialization parameters are summarized in the following table:
Certain initialization parameters are critical at database creation or affect certain database operations. These parameters must have the same value for every instance in an Oracle Parallel Server specified in each INITDB_NAME.ORA file for each instance. For example, the values of DB_BLOCK_SIZE and CONTROL_FILES must be identical for every instance.
The following initialization parameters must have identical values (unless noted otherwise) for every instance in an Oracle Parallel Server.
Set values for the LM_* initialization parameters. Note that the resources, locks and processes configurations are per Oracle Parallel Server instance. For ease of administration, these parameters should be consistent for all the instances.
Chapter 18, "Administering Multiple Instances," of the Oracle8i Parallel Server Concepts & Administration includes descriptions of the initialization parameters.
The database for which the instance is started must have access to the appropriate initialization parameter files. Oracle Parallel Server uses the initialization parameter files located in:
To customize Oracle Parallel Server databases functions, you need to edit the initialization parameter files. Use any ASCII text editor to modify the files.
Oracle Parallel Server Management allows you to perform a variety of management tasks on your Oracle Parallel Servers, distributed systems, and databases. The Enterprise Manager Console provides a central point of control for the Oracle environment through an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) that provides drag-and-drop system management.
The Console enables you to manage a heterogeneous environment as easily as a homogeneous one. You can schedule jobs on multiple nodes simultaneously or monitor groups of services together.
A database or system administrator can thus handle all nodes in an Oracle Parallel Server as a single entity. For example, you can configure Oracle Enterprise Manager to execute a job across all nodes of an Oracle Parallel Server.
This section is meant to only describe Oracle Enterprise Manager administration for Oracle Parallel Server. Use this section as a supplement to general information contained in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide. This section covers the following topics:
See Chapter 5, "Installing and Configuring Oracle Parallel Server Management", for configuration information.
To use the Console, start the following components:
See "Step 4: Start Oracle Enterprise Manager Components" for instructions.
From the Navigator window, you can view and manage both single-instance and multiple-instance databases. The information available for Oracle Parallel Servers is the same as for single-instance databases.
The Navigator displays all the network objects and their relationships to other objects including a direct view of objects such as user-defined groups, nodes, listeners, servers, databases, and database objects.
From the Navigator window, Oracle Parallel Servers are located in the Databases folder which contains entries for single-instance and Oracle Parallel Server databases. Each Oracle Parallel Server folder contains the objects for data files, in-doubt transactions, profiles, redo log groups, roles, rollback segments, schema objects, tablespaces, and users.
|
Note: : If preferred credentials were not set for the database, as described in "Step 6: Specify Preferred Credentials for Nodes and Oracle Parallel Server Database", the Database Connect Information dialog prompts you to enter database connect information. |
An Oracle Parallel Server database's subfolders, such as Datafiles and Users, behave just as they do for single-instance databases. By right-clicking the mouse on these objects, property sheets can be accessed to inspect and modify properties of these object just as for single-instance database. For example, right-clicking on the Redo Log Groups folder and choosing Create to add a new redo log group
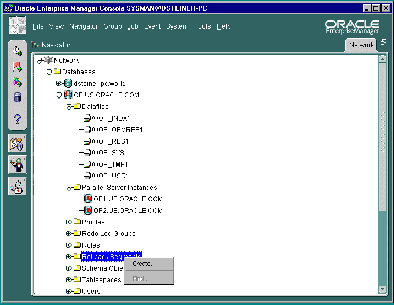
The Oracle Parallel Server database and each discovered Oracle Parallel Server node contains a Parallel Server Instances folder that can be expanded to display the instances belonging to the database or node.
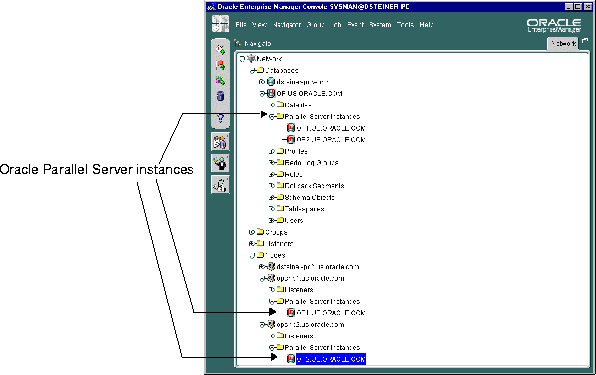
Right-clicking on a Oracle Parallel Server brings up the Oracle Parallel Server right-mouse menu:
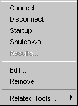
This menu contains entries for the following functions:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Connect |
Connects to the database. In the Database Connect Information dialog box, enter the database user name, password and privileges. If you want to perform a startup or shutdown, a user with SYSDBA privileges must be specified. |
|
Disconnect |
Terminates a connection to the database. |
|
Startup |
Starts the database. See "Starting an Oracle Parallel Server Database" for Oracle Parallel Server-related instructions. |
|
Shutdown |
Shuts down the database. See "Shutting Down an Oracle Parallel Server Database" for Oracle Parallel Server-related instructions. |
|
Results |
Displays startup and shutdown results, as described in "Viewing the Parallel Server Operation Results". |
|
Edit |
Allows inspection of the state of the Oracle Parallel Server, including which instances are active. See "Viewing Oracle Parallel Server Status" for Oracle Parallel Server-related instructions. |
|
Remove |
Deletes the database object and its related services. This should only be performed if it is no longer necessary to monitor or manage a database from Oracle Enterprise Manager. |
|
Related Tools |
Contains access to other tools which have been enabled for Oracle Parallel Server. |
The Console allows you to start an Oracle Parallel Server database or individual instances.
Once all Oracle Parallel Server instances are up, the Oracle Parallel Server database is considered to be up.
To start up an Oracle Parallel Server database:
A menu appears with options for the database.
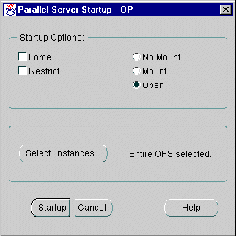
The Parallel Server Startup dialog box appears.
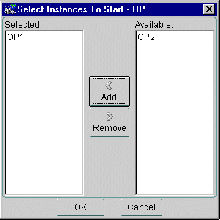
The Select Instances to Start dialog box appears:
The Parallel Server Operation Results dialog box displays the progress of the startup operation, as described in "Viewing the Parallel Server Operation Results".
If the instances were started successfully, the Parallel Server Started message dialog box appears with a successful message:
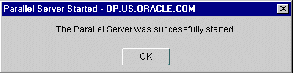
Click OK in the Parallel Server Started message to acknowledge the message, then click Close in the Parallel Server Operation Results.
If the startup fails, the Parallel Server Started message box appears with a failure message. Click View Details to view more information in the Parallel Server Operation Results dialog about why the shutdown failed, then click Close.
The Console allows you to shut down an Oracle Parallel Server database or individual instances.
Once all Oracle Parallel Server instances are shut down, the Oracle Parallel Server is considered to be shut down.
To shut down an Oracle Parallel Server database:
A menu appears with options for the database.
The Parallel Server Shutdown dialog box appears.
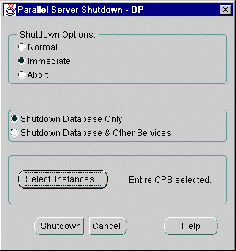
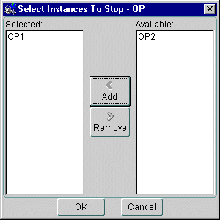
The Select Instances to Stop dialog box appears:
The Parallel Server Operation Results dialog box displays the progress of the shutdown operation, as described in "Viewing the Parallel Server Operation Results".
If the instances were shut down successfully, the Parallel Server Stopped message dialog box appears with a successful message.:

Click OK in the Parallel Server Stopped message to acknowledge the message, then click Close in the Parallel Server Operation Results.
If the shutdown fails, the Parallel Server Stopped message box appears with a failure message. Click View Details to view more information in the Parallel Server Operation Results dialog about why the shutdown failed, then click Close
The Parallel Server Operation Results dialog displays information about the progress of the instance startup or shutdown operation you selected:
The operation results are presented in two views:
The Parallel Server Operation Results dialog box automatically displays during a startup or shutdown operation. It may also be initiated with the following steps:
A menu appears with options for the database.
While the startup operation is running against an Oracle Parallel Server running on a UNIX system, the Status Details tab progress display is shown, with the status of object startup, and updated dynamically as the operation progresses:
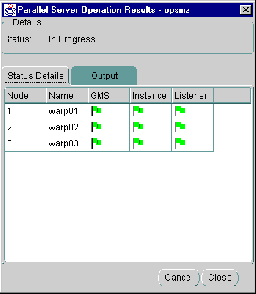
The services managed by Oracle Parallel Server Management vary by platform and by version. The Oracle Parallel Server being managed in this example is release 8.0.4, so the GMS (Group Membership Service) is being started. In release 8.1, the GMS is built into the RDBMS kernel, so only instance and listener columns display.
When shutting down a Oracle Parallel Server, the tab displays only those nodes and instances that are being affected by the shutdown operation.
The following are the possible states that each component may experience:
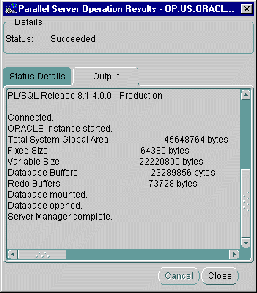
The Output tab displays the commands executed by the Oracle Parallel Server node and any associated error messages in textual format.
The Edit Parallel Server dialog box displays status information about the parallel database, such as instances available in the Oracle Parallel Server and status of Oracle Parallel Server components.
To view status information about an Oracle Parallel Server database:
A menu appears with options for the database.
The Edit Parallel Server dialog box appears.
The operation results are presented in two views:
The Status tab displays information about the currently running instances by querying V$ACTIVE_INSTANCES table. Oracle Enterprise Manager makes a connection to the Oracle Parallel Server, therefore, this tab will not appear if the Oracle Parallel Server is down.
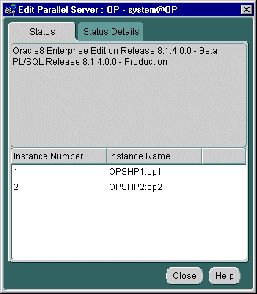
|
Note: This tab is not available for a Windows NT Oracle Parallel Server, because OPSCTL on Windows NT does not generate status details. |
Displays an overall view of the state of the Oracle Parallel Server and related components. This tab displays the status of the various components, such as listeners, and instances for all nodes.
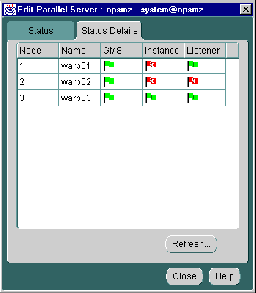
The following are the possible states that each component may experience:
The job scheduling system provides a highly reliable and flexible mechanism for DBAs to schedule and automate repetitive jobs on both the Oracle Parallel Server database and Oracle Parallel Server instances.
The Console contains a full-featured scheduling tool which allows DBAs to come up with a customized schedule. This provides DBAs with true "lights out" management capability so that they can focus on other tasks. A rich selection of jobs is provided for Oracle Parallel Servers.
You can create a job with a Oracle Parallel Server database or an Oracle Parallel Server instance as the destination. To create a new job, follow these steps:
From the Create Job property sheet, you can specify the details of a new job. The Create Job property sheet contains these tabs:
The following tabs contain Oracle Parallel Server-specific options:
See the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for general job scheduling information.
From the General tab, specify the:
The General tab contains these options:
From the Tasks tab, choose the task(s) that you want the job to perform. The list of tasks that appear is different depending on whether you select an Oracle Parallel Server or an Oracle Parallel Server instance as your Destination Type from the General tab.
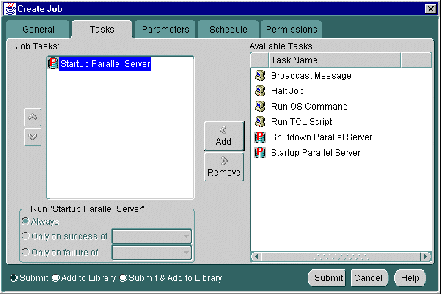
Move the tasks between the Available Tasks and Selected Tasks lists with the Add and Remove buttons.
If your Destination Type is a Parallel Server, you can choose from these tasks:
If your Destination Type is a Parallel Server Instance, you can choose from these tasks:
For a description of these tasks and the parameters you need to set, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
From the Parameters tab, you can specify parameter settings for the job tasks you selected on the Tasks tab. The parameters which display vary according to the job task. Parameters for Oracle Parallel Server startup and shutdown tasks are described below. To find out what parameters you need to set for Oracle Parallel Server instance tasks, refer to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
When you select the Startup Parallel Server task on the Tasks tab, the following displays:
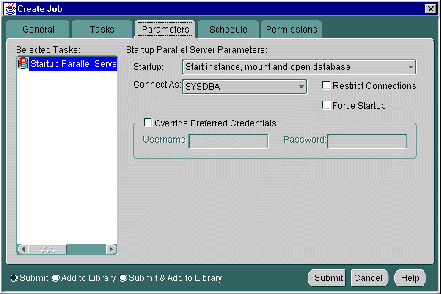
Complete the parameters on the tab and click the Submit button to run the Oracle Parallel Server startup task.
The Parameters tab for Startup contains these options:
When you select the Shutdown Parallel Server task on the Tasks tab, the following displays.
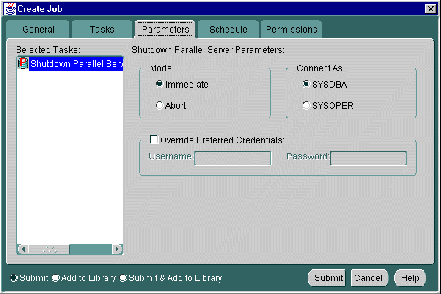
Complete the parameters on the tab and click the Submit button to run the Oracle Parallel Server startup task.
The Parameters tab for Shutdown contains these options: